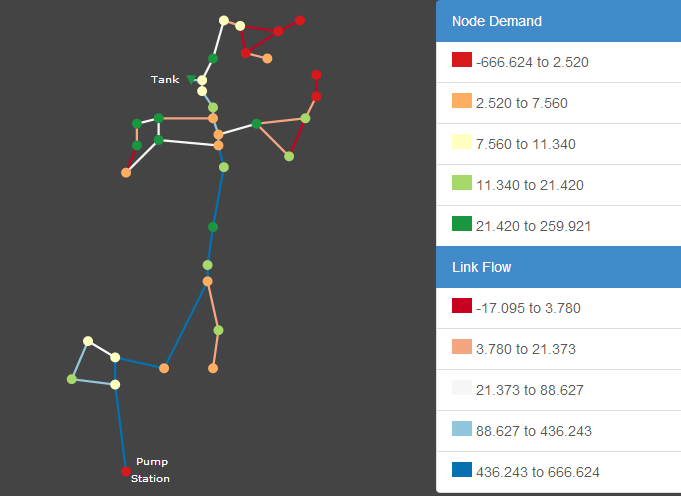
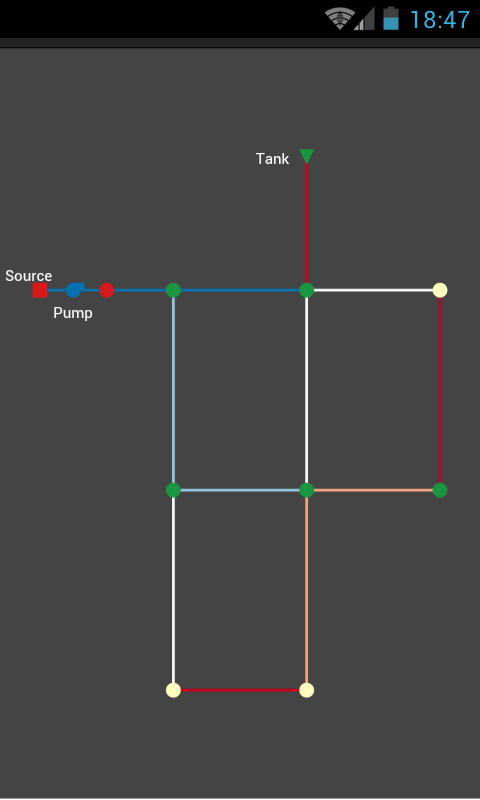
From the conference web-site:
CleanTech 2014 is the 18th annual international event for Clean Technologies: environmental quality, infrastructures and green building, renewable energy and water technologies. The exhibition will take place at “Avenue” Convention and Events Center, Israel
The 18th International Summit and Exhibition for Renewable Energy and water Technologies, Recycling and Environmental Quality, Infrastructure and Green Building
CleanTech 2014 is the 18th annual international event for Clean Technologies: environmental quality, infrastructures and green building, renewable energy and water technologies. The exhibition will take place at “Avenue”- Congress and Exhibition Centre, Air Port City, Israel. CleanTech Exhibition has gained the status of a high quality international business platform, where companies, researchers and professionals display their newest developments, novel technologies and outstanding quality services in the fields of environmental protection and green solutions, infrastructure, renewable energy, waste treatment, water technologies for treatment, desalination, harvesting, purification, filtration and more. During the exhibition, there are professional conferences, seminars and symposiums, in which executives come to learn.
Exhibition Segments
Water Technologies, Industrial & Municipal Solutions
The Expo shall display technologies and solutions for:
Water Supply & Purification
Analysis & Instruments: Metering, Sampling, Testing, Monitoring, Data Logging.
Water Sources, Hydrologic Engineering, Reservoirs, Protection etc.
Water Distribution: Valves, Pumps, Irrigation, Pipe works etc.
Filtration, Purification & Conditioning Technologies
Demineralization: Desalination, Distillation Evaporation etc.
Waste Water Treatment
Domestic: Grey Water Recycling, Biological Remediation etc.
Industrial: Recovery, Cleaning, Recirculation
Waste Water Plant Design, Engineering and Construction Services
Waste Efficiency Devices
Water Management, Security and Flow Control
Renewable Energy
Global investment in renewable energy sets new records every year, according to a reports released by the Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century (REN21). Technologies such as wind, solar, biomass, geothermal, and small hydro now provide hundreds of gigawatts of electricity generating capacity. Subsequently renewable energy markets have been growing robustly. According to the forecasts the market capacity may at least double itself within a relatively short period of time.
The steep rise in air pollution and oil prices has spurred the development of energy alternatives that will reduce dependency on expensive, environment-polluting oils. Israel must keep abreast with the developed countries and increase its use of renewable energies. The Exhibition promotes the technologies in this crucial area.
New Israeli incentives program for solar photo-voltaic systems
The Israeli Public Utility Authority (PUA) published on June 2nd 2008 the new incentives program for solar photo-voltaic systems.
Summary of the program:
– Feed in tariff of 2.01 NIS per each KWh produced.
– Residential systems up to 15KWp, commercial up to 50KWp.
– Contract for 20 years.
– Size of the system is limited to the size of the electricity connection of the site.
Green Building
In recent years there has been a growing awareness of “green construction,” that is, building that provides a higher quality of life and healthier environment by cutting back on the overall bad effects on the environment from the process of construction and building use. The exhibition will emphasize the environment as a central factor in the planning and implementation of green construction projects.
Natural Gas
Gas demand, which is rising at a slightly faster rate than oil, is currently being drived by rapid growth as a fuel for clean and efficient electric power generation. As with oil, gas resource additions have exceeded demand for most of the last century. Much of this supply was discovered between roughly 1960 to about 1980. This was driven by major discoveries in Russia, the Middle East, the Netherlands and Indonesia.
Noble Energy, Inc. has announced a natural gas discovery at the Tamar prospect in the Matan license, offshore Israel. The Tamar #1 well, located in approximately 5,500 feet of water, was drilled to a total depth of 16,076 feet to test a subsalt, lower-Miocene structure in the Levantine basin. Formation logs identified more than 460 feet of net pay in three high-quality reservoirs. The thickness and quality of the reservoirs encountered were greater than anticipated at the well location. Preliminary estimates indicate that the Tamar field might contain over 88 billion cubic meters of gas.
Israel has begun setting up a natural gas system to provide this energy source to industrial plants and national and privately owned power stations throughout the country. The expo will also display technologies for transporting oil and gas that are safety guaranteed and environmentally friendly.
Waste and Recycling
Recycling is an economic development tool as well as an environmental tool. Reuse, recycling, and waste reduction offer direct development opportunities for communities. According to different sources the worldwide recycling industry employs the skills of more than 1.5 million employees as well as using a great armoury of sophisticated machinery. With a total annual turnover exceeding US$ 160 billion, it is also a capital-intensive business. Annual investments and R&D in the recycling industry amount to around US$ 20 billion. Each year, the global recycling industry processes more than 600 million tonnes of commodities such as ferrous and nonferrous metals, paper, plastics, textiles, glass, tyres and much more. CleanTech 2012 will display cutting-edge technologies and solutions for this industry.
Air Pollution
The contamination of the air we breathe is the curse of the developed countries. Special factors in Israel, such as population density, the continuous rise in the standard of living, and meteorological conditions exacerbate the problem. Unfortunately Israel lags far behind the first world in the treatment of air pollution and the effects that can cause disease and suffering. The exhibition management targeted this area for special concern by raising public awareness of the need to cope with this problem seriously.
The 18th CleanTech exhibition, 18-19 February 2014, “Avenue”- Congress and Exhibition Centre, Air Port City, Israel
For Early Registration press here
E-mail: info@mashov.net
tel: +972 – 8 – 6273838
Fax: + 972 – 8 – 6230950
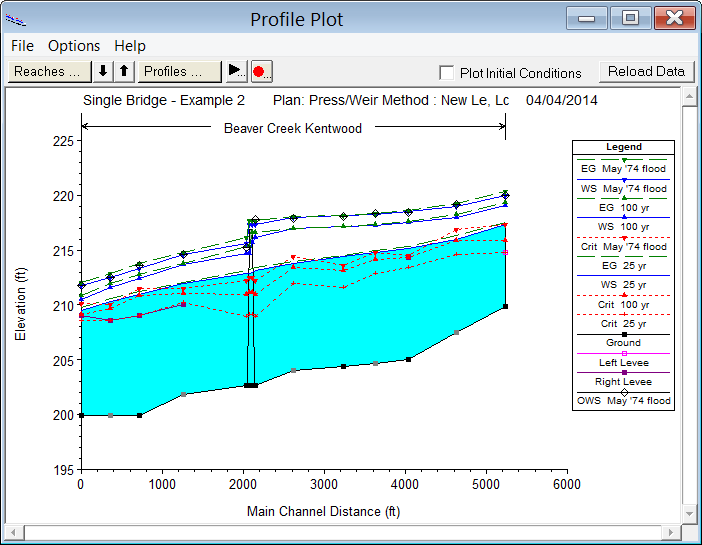 Download RasClient here (ZIP file ~62KB)
Download RasClient here (ZIP file ~62KB)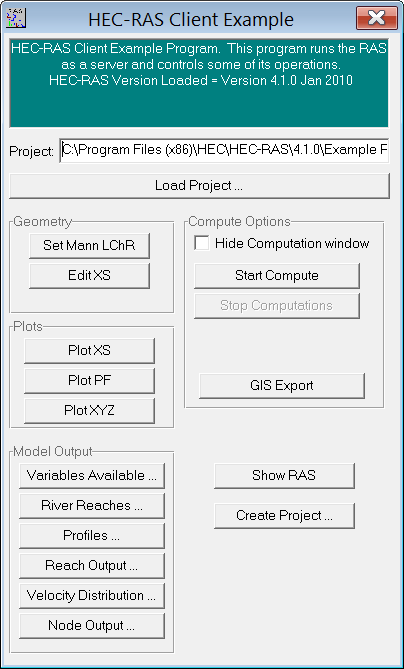
 The
The  During the
During the