Flow Calc – Open Channel Flow hydraulic calculations
Flow Calc is a commercialֲ ֲ computer software program designed to calculate common Open Channel Flow hydraulic characteristics using only the methods of the Manning’s Equation for regular and irregular channel geometries for steady uniform flow including circular and elliptical pipes.
From Flow Calc web site:
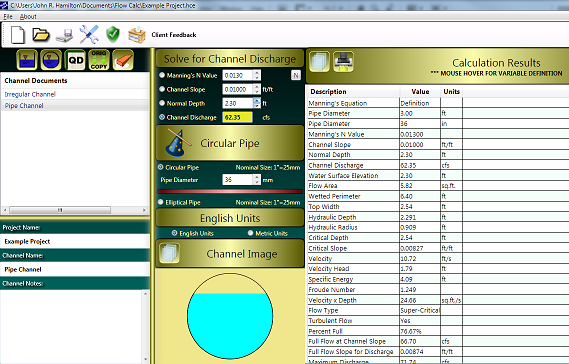
Flow Calc provides an easy to use interface that is streamlined and simplified for both English and SI Units. Extensive efforts were undertaken to provide a single screen interface to provide the most functionality for the design engineer. Effectively this allows the design engineer to monitor and correct channel geometries on the fly while at the same time being able to view the computational results immediately. Along with the data input controls for manual data entry, spin-controls are additionally provided to facilitate design review dynamically. A graphical representation of the channel geometry as entered by the design engineer provides a visual aide of the water surface elevation that is continually adjusted based upon input values.
 On 1941 the Arab Mufti of Jerusalem Haj Amin al-Husseini met with Adolf Hitler and discussed ways to ‘solve the Jewish problem’. Three years later the Nazis and the Arabs of Palestine planned to poison the drinking water in Tel-Aviv with Arsenic poison.
On 1941 the Arab Mufti of Jerusalem Haj Amin al-Husseini met with Adolf Hitler and discussed ways to ‘solve the Jewish problem’. Three years later the Nazis and the Arabs of Palestine planned to poison the drinking water in Tel-Aviv with Arsenic poison.