Optimizing Pumping Systems Article
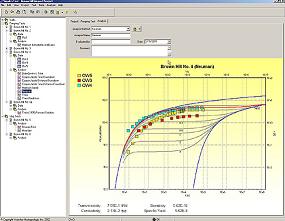
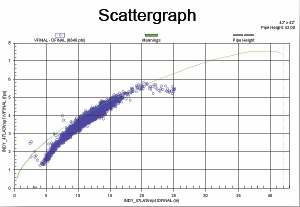
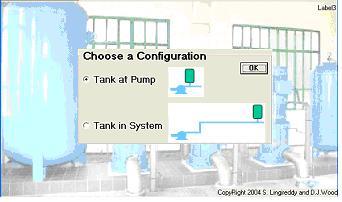
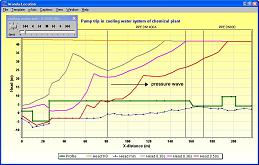
With pumping systems accounting for about 20% of the world’s energy usage, a great potential for cost and energy savings exists within such systems. Unfortunately, pumping system design engineers work in an environment where budget and schedule constraints limit their ability to optimize their systems using traditional methods. “Optimizing Pumping Systems To Minimize First Or Life-Cycle Cost”, featured in the October 2002 issue of Pumps & Systems magazine, describes the new technology of IntelliFlowֲ® embodied in AFT Mercury that now allows the systems engineer to truly optimize the sizing of their systems’ piping and components resulting in huge savings potentials. Jointly authored by Trey Walters of AFT and Judy Hodgson of Dupont, the article also presents several real world examples where life cycle cost savings of up to 70% were achieved. The Pumps & Systems article was derived from “Optimizing Pumping Systems to Minimize First or Life-Cycle Cost”, presented to the 19th International Pump Users Symposium.
You can find the full text of this original paper by clicking here.